0 Introduction
0-0 概念
- JPBC, which is the short of Java Pairing-Based Cryptography Library.
- JPBC API 网址: API
- 基于配对的密码学,这里的配对指双线性配对,有关双线性对性质见《现代密码学》杨波,第四版,P107。
- Pairing for Cryptography definition from DEFINITION
0-1 性质
- 主要性质: 双线性(Billinearity) & 非退化性(Non-degeneracy)

0-2 实例
Elements belonging to an algebraic structure (groups, rings and fields) are accessible through the Element interface that represents a mutable value.
//Code Example: Field G1 = pairing.getG1(); Element g = G1.newRandomElement();Pairing Parameters Generators, JPBC provides a set of interfaces and classes to generate and manage the parameters that describe a pairing setting. The PairingParametersGenerator interface is the starting point. Once an instance of such interface has been created then pairing parameters can be generated by invoking the generate method as follow:
import it.unisa.dia.gas.jpbc.PairingParametersGenerator; import it.unisa.dia.gas.jpbc.PairingParameters; //Initialize the pairing parameters generator. ParametersGenerator parametersGenerator = ... //Then, generate the parameters by invoking the generate method. PairingParameters params = parametersGenerator.generate();
注:JPBC提供的一些default配对参数,详见PARAMETERS
1 Interface
1-0 API
API详见API
重要的3个接口Pairing, Filed, Element

1-1 配对 Pairing
默认实例化:
1 | Pairing pairing = PairingFactory.getPairing("params.properties"); |
随机实例化:
1 | PairingParameters pg = new TypeACurveGenerator(rBits, qBits).generate(); |
配对操作:
1 | //There are Elements g1 and g2, Element a = e(g1, g2) |
1-2 群 Field
详细的解释是algebraic structure (groups, rings and fields)
实例化需通过Pairing对象,别问为什么,不知道为什么这么设计
1 | //Return Zr |
1-3 元素 Element
Field中的元素
1 | Element e = pairing.getG2().newRandomElement(); //随机 |
1-4 运算
1 | add() //加 |
详细的用法查看详细的API
2 Configure
2-0 下载JAR包
地址:JPBC Source
点击Download后需要等待一段时间(有可能需要几分钟)
解压后
- jars文件夹中是相应需要使用的jar包,里面是已经编译好的字节码文件
- jpbc-*是相应的.java文件,so我们能get源码并追踪一些乘方计算为什么不那么耗时了
- params文件夹中是关于双线性对(或者说是椭圆曲线)的配置文件
- 里面有两个文件夹“curves”和“mm/ctl13”
- 总的来说,这两个文件夹内都是一些.properties配置文件
- 目前使用的是curves里面的一些配置文件
- 关于配对类型详解可以参考李发根的《基于配对的密码学》中P24
2-1 配置过程
在项目中根目录下新建lib文件夹,将所需要的jar文件拷贝到lib中
然后右键 项目文件 –> Build Path –> Configure Build Path
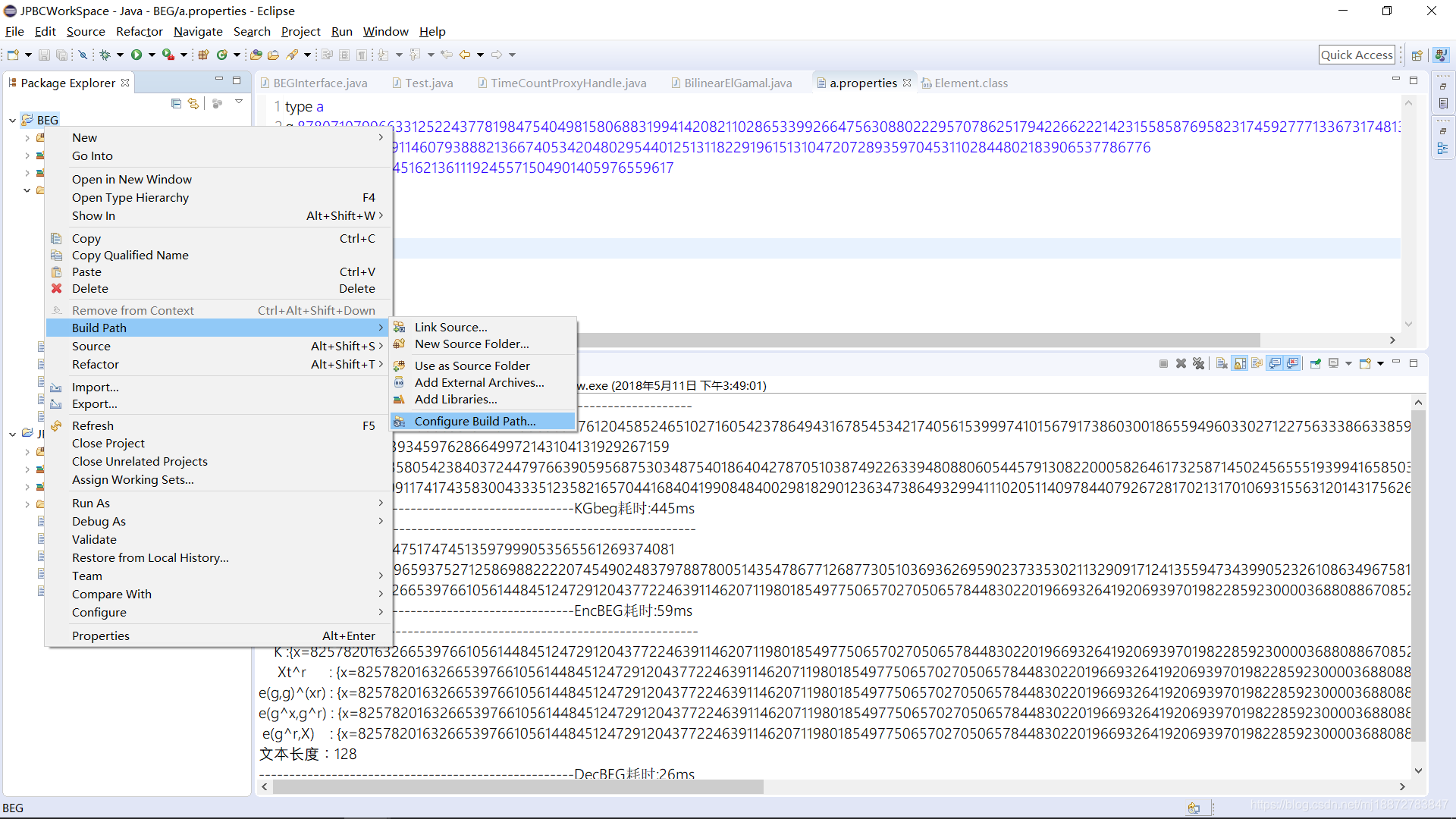
弹出一下对话框后点击Libraries
从刚刚的lib中Add JARs